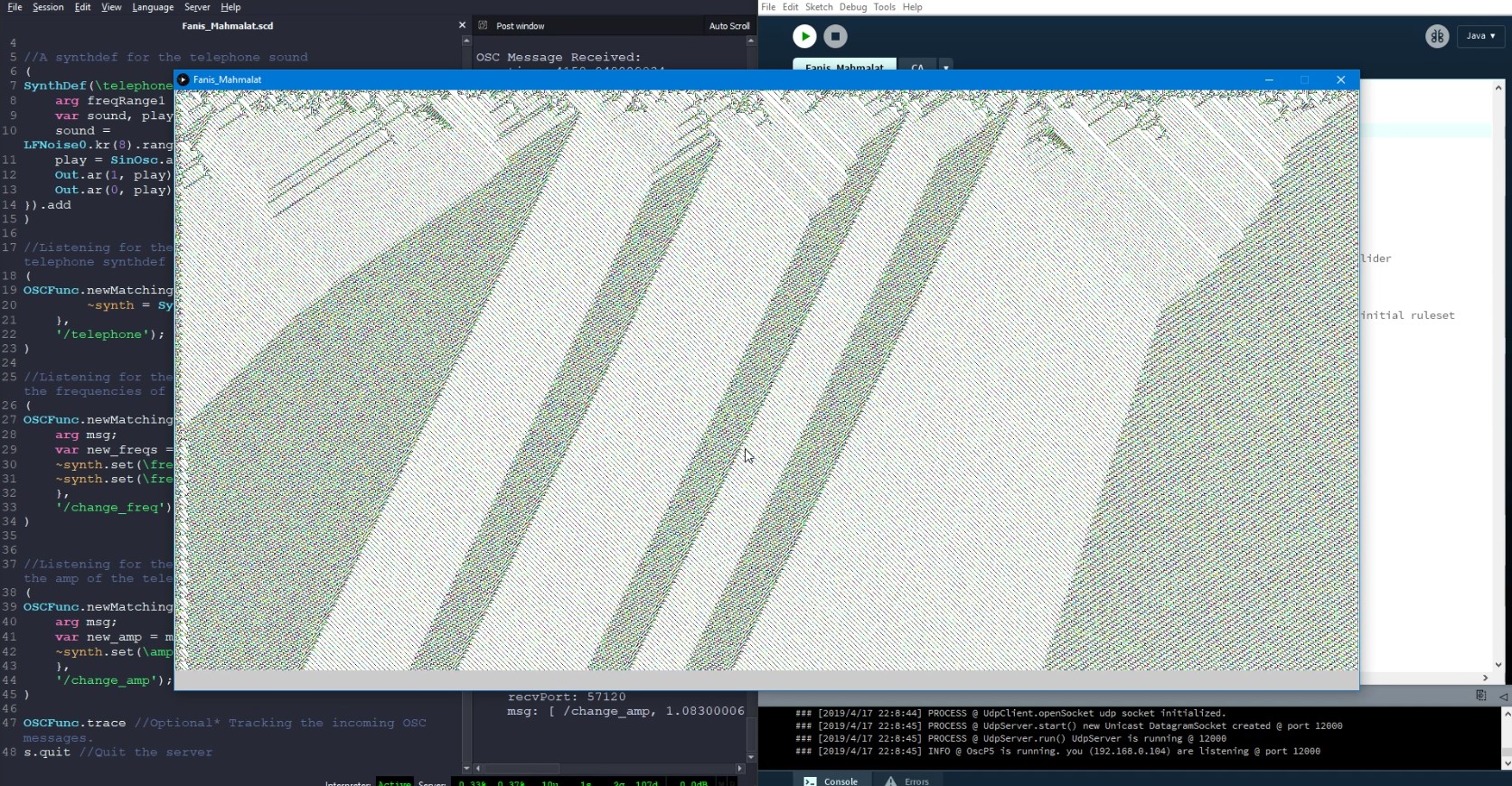
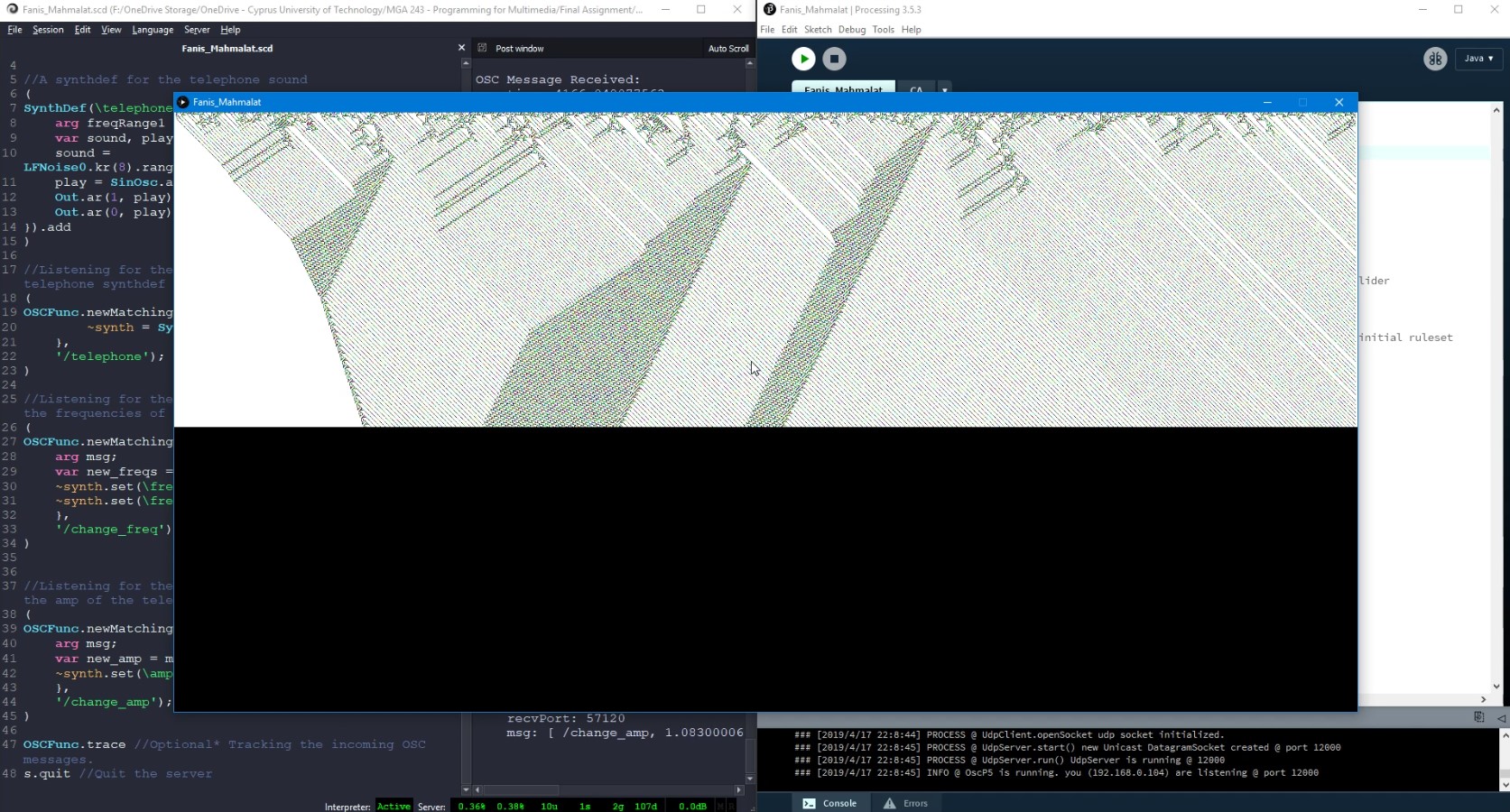
A cellular automaton (pl. cellular automata, abbrev. CA) is a discrete model of computation studied in automata theory. Cellular automata have found application in various areas, including physics, theoretical biology and microstructure modeling. A cellular automaton consists of a regular grid of cells, each in one of a finite number of states, such as on and off. The grid can be in any finite number of dimensions. For each cell, a set of cells called its neighborhood is defined relative to the specified cell. An initial state (time t = 0) is selected by assigning a state for each cell. A new generation is created (advancing t by 1), according to some fixed rule (generally, a mathematical function) that determines the new state of each cell in terms of the current state of the cell and the states of the cells in its neighborhood.